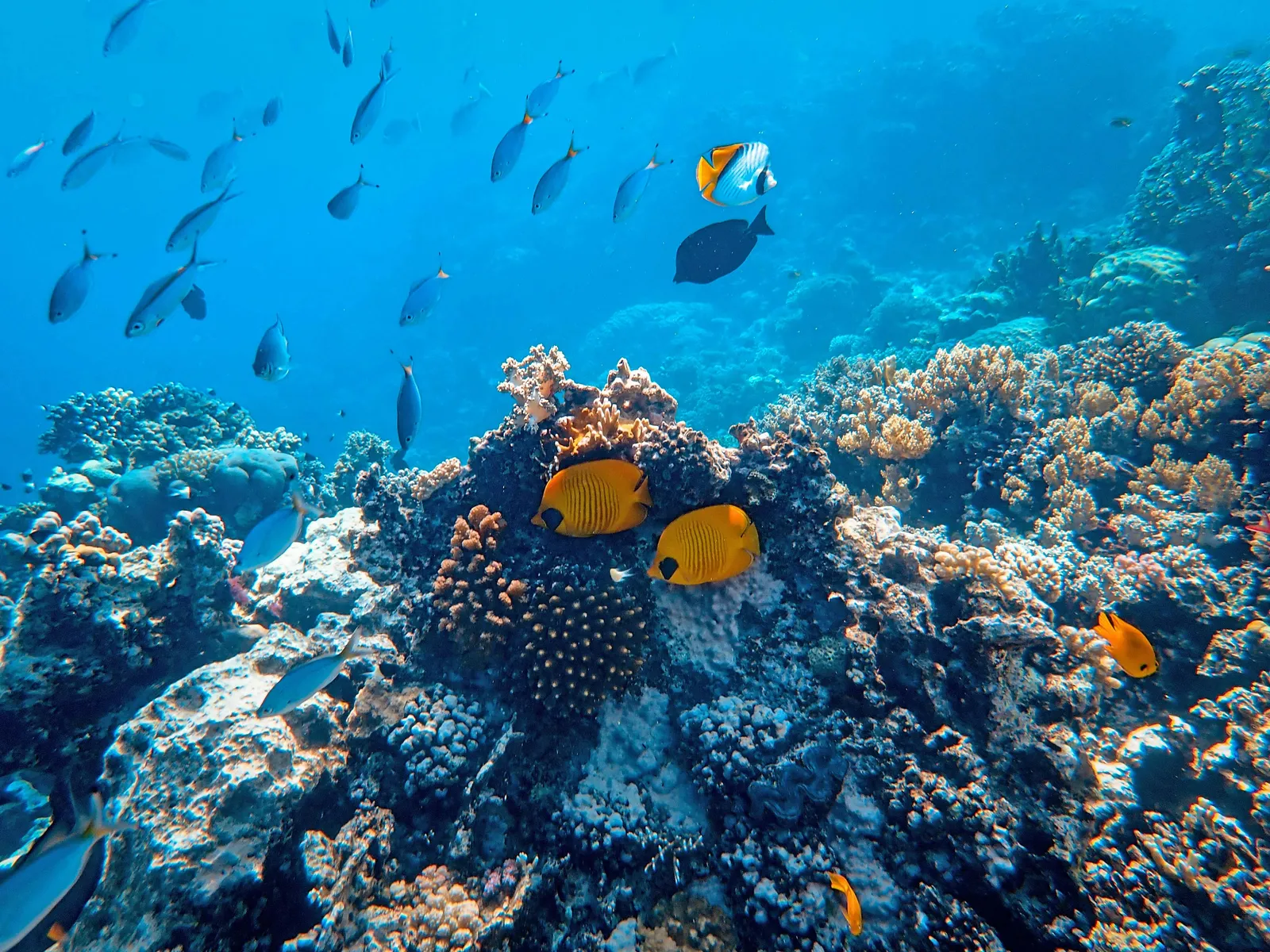
Biodiversity and Habitat Monitoring Using EyeROV's Advanced Underwater ROVs
Explore how EyeROV's cutting-edge ROVs are revolutionizing biodiversity and habitat monitoring. Learn how advanced imaging, sonar technologies, and eco-friendly operations are making underwater research more efficient, safer, and sustainable.
Life underwater is truly fascinating and worth exploring. Underwater habitats or ecosystems commonly refer to the complex communities of organisms and their physical environment in aquatic habitats.
These ecosystems can be found in various bodies of water, including oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, and even underground aquifers. They are essential for supporting marine life and play a crucial role in maintaining the overall health of our planet.
Need for Biodiversity and Habitat Monitoring
Conservation of biodiversity and habitat is crucial, as it helps maintain the stability of the ecosystem. A large portion of the population depends on underwater biodiversity and natural habitats for food, medicine, renewable resources, and other economically valuable assets.
Drastic environmental changes directly influence aquatic biodiversity. Since marine life depends on many other living organisms and the overall health of the planet, it must be preserved for future generations.

The major threats to biodiversity and habitat include climate change, pollution, and human activities. Therefore, continuous monitoring of biodiversity and habitat is essential to safeguard these ecosystems.
Conventional Ways for Monitoring Biodiversity and Habitat and Their Limitations
There are numerous traditional ways to monitor habitat and biodiversity. One common method is using underwater cameras operated by divers.
However, diver-based inspections pose many risks, especially because some life forms inhabit deeper waters where divers struggle to operate safely. Harsh aquatic conditions at great depths further complicate the collection of data using divers.
Additionally, the security and well-being of both the divers and the aquatic environment must be considered. Accuracy, quality, and coverage of data are also significant concerns with traditional methods, which tend to be time-consuming and intricate.
To effectively preserve biodiversity and habitats, knowing the exact geographic locations of these life forms is critical.
Monitoring Using ROVs

All underwater inspections can be efficiently performed using Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs). ROVs simplify deep-water navigation and enable real-time data collection.
Equipped with HD cameras and powerful lighting, ROVs capture high-quality images even in challenging underwater conditions. Various sensors and payloads, such as imaging sonar, side scan sonar, and USBL systems, can be integrated with ROVs to enhance data collection capabilities.
Safety guards and shields are also incorporated to protect both the ROV and the environment being inspected.
Details of Sensors and Payloads Used
Imaging SONAR
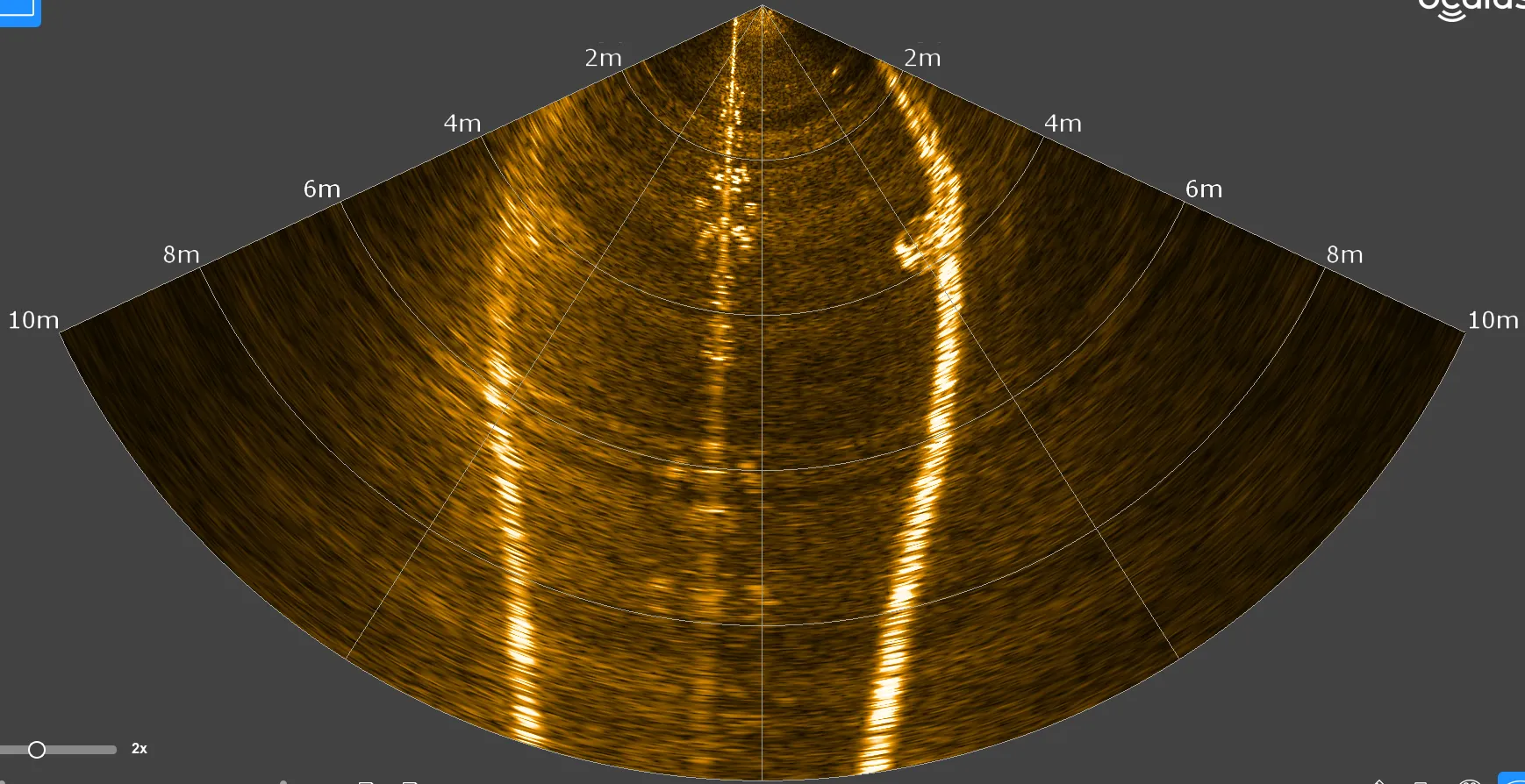
Imaging SONAR captures acoustic images even in turbid water conditions, proving highly effective when visibility is poor.
Side Scan SONAR
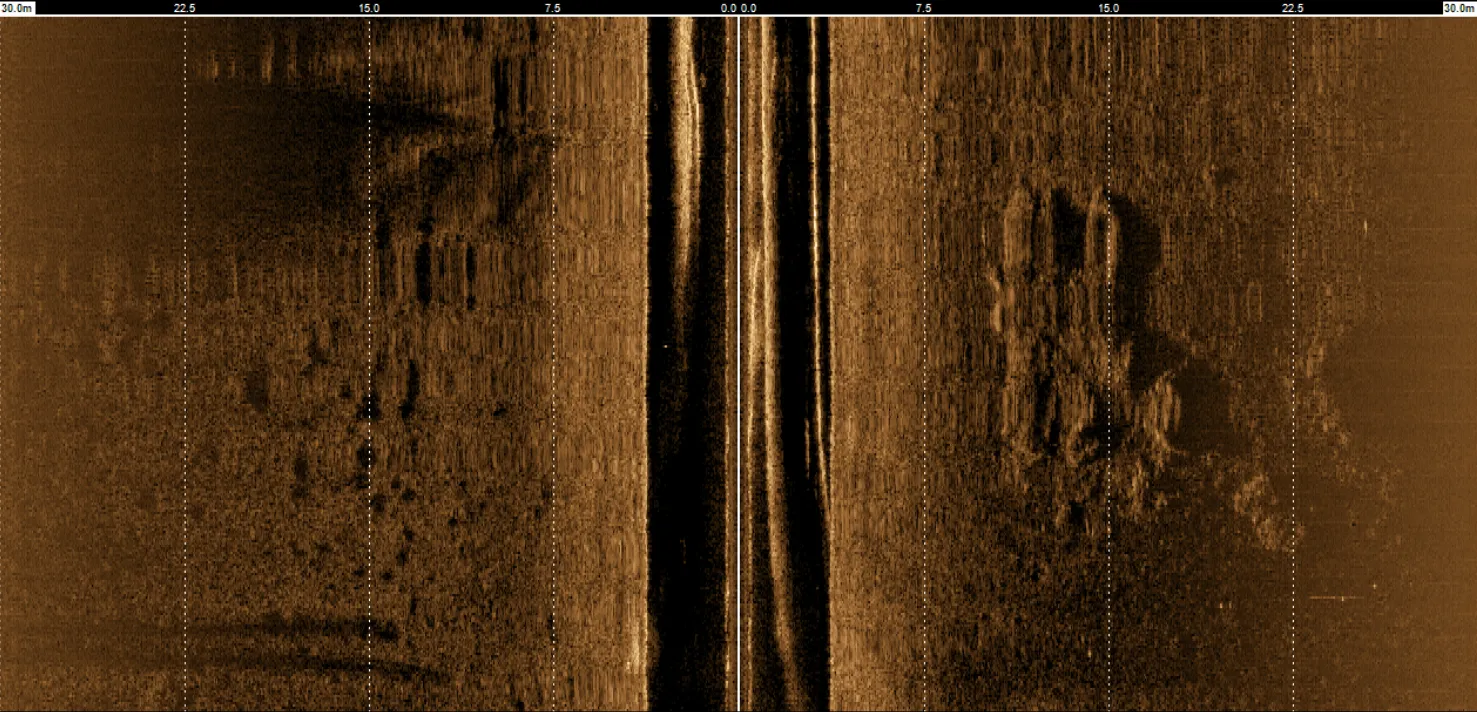

Side-scan SONAR helps identify surface features of the seafloor and is essential for seabed mapping.
USBL
The Ultra Short Baseline (USBL) system efficiently provides the exact geographic coordinates of underwater lifeforms. Visual camera outputs can be overlaid with these location coordinates for better documentation.
In addition to these payloads, ROVs can also capture depth and temperature data of the underwater environments they inspect.
Methodology
The area covered by an ROV survey varies depending on operational factors, scheduled surveys, sampling windows, and the depth of the survey area.
Different types of search patterns may be used depending on the survey’s goals. If anchored or using a shot line (in shallow waters), more complex search patterns can be deployed.
An umbilical cable or tether ensures bi-directional communication between the ROV and the surface. Pilots steer the ROV using a command and control system equipped with joysticks for tilting and rotating the cameras, adjusting brightness, and controlling depth and direction.
A co-pilot supports navigation, interpreting visuals and providing instructions to the pilot. The control station receives real-time visual and sonar data streamed from the ROV.
Results and Videos
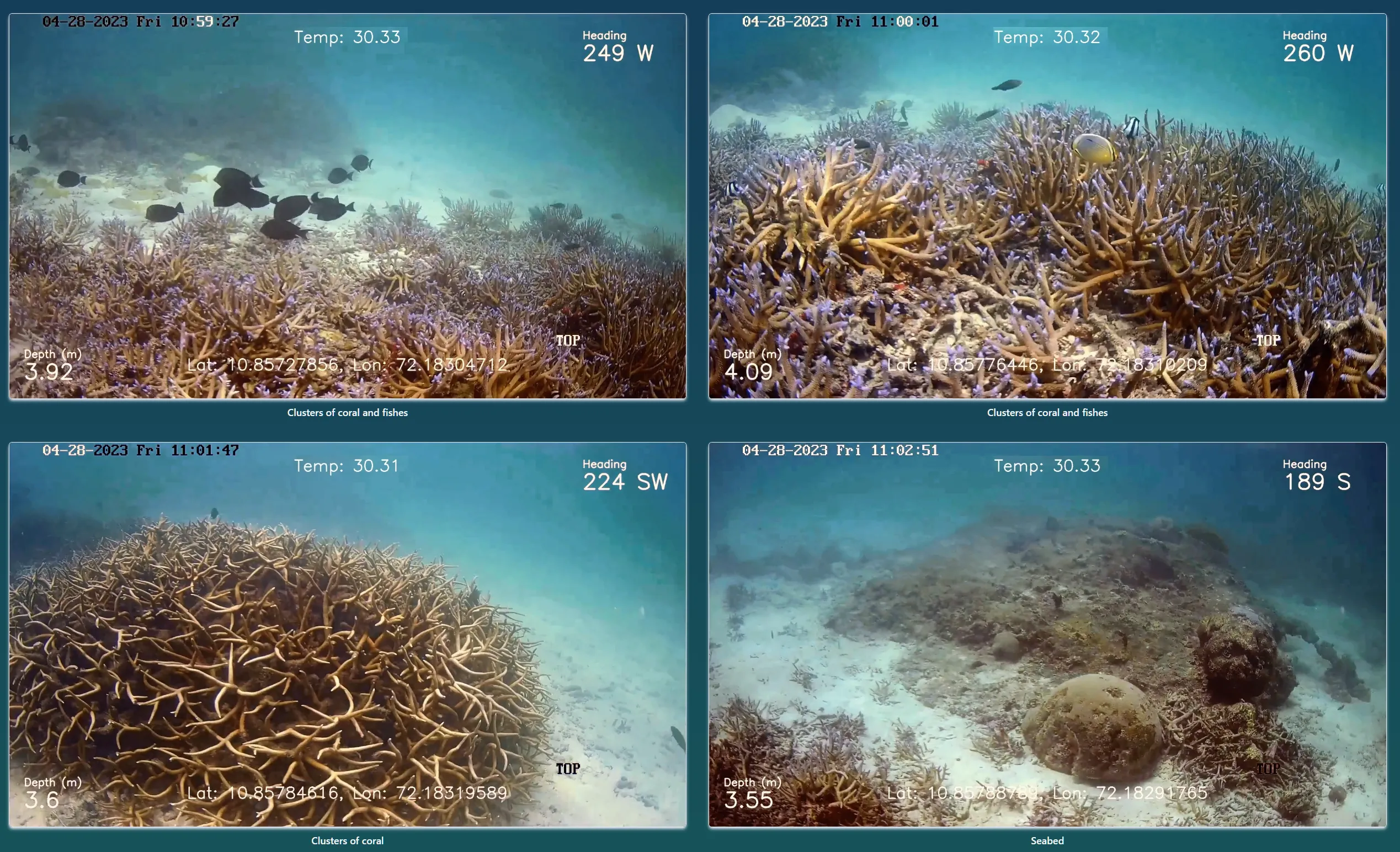

The ROV captures underwater images and video footage showcasing a diverse range of marine biodiversity, including fish populations and coral reefs.
Camera footage can be overlaid with additional data such as geographical coordinates and temperature readings. From these recordings, researchers can better understand the characteristics and traits of coral reefs and assess fish populations.
EyeROV in Ocean and Underwater Research
EyeROV’s ROVs can reach deep waters and gather vital information about underwater lifeforms. They are becoming essential tools for expanding knowledge about the abundance and distribution patterns of deepwater habitats, including cold-water corals, without damaging these sensitive environments.
The data collected by EyeROV ROVs enables geographers and scientists to further study biodiversity and the evolution of marine life. It also provides crucial insights into the exact condition of underwater ecosystems.
EyeROV ROVs are incredibly eco-friendly and do not pollute the environment in any way. They are ideally suited for biodiversity and habitat inspection, as they operate from a safe distance without harming any lifeforms.
By leveraging advanced sensors and cameras, EyeROV’s technology is paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries and the conservation of aquatic ecosystems.
Learn More about EyeROV’s Maritime Services.